
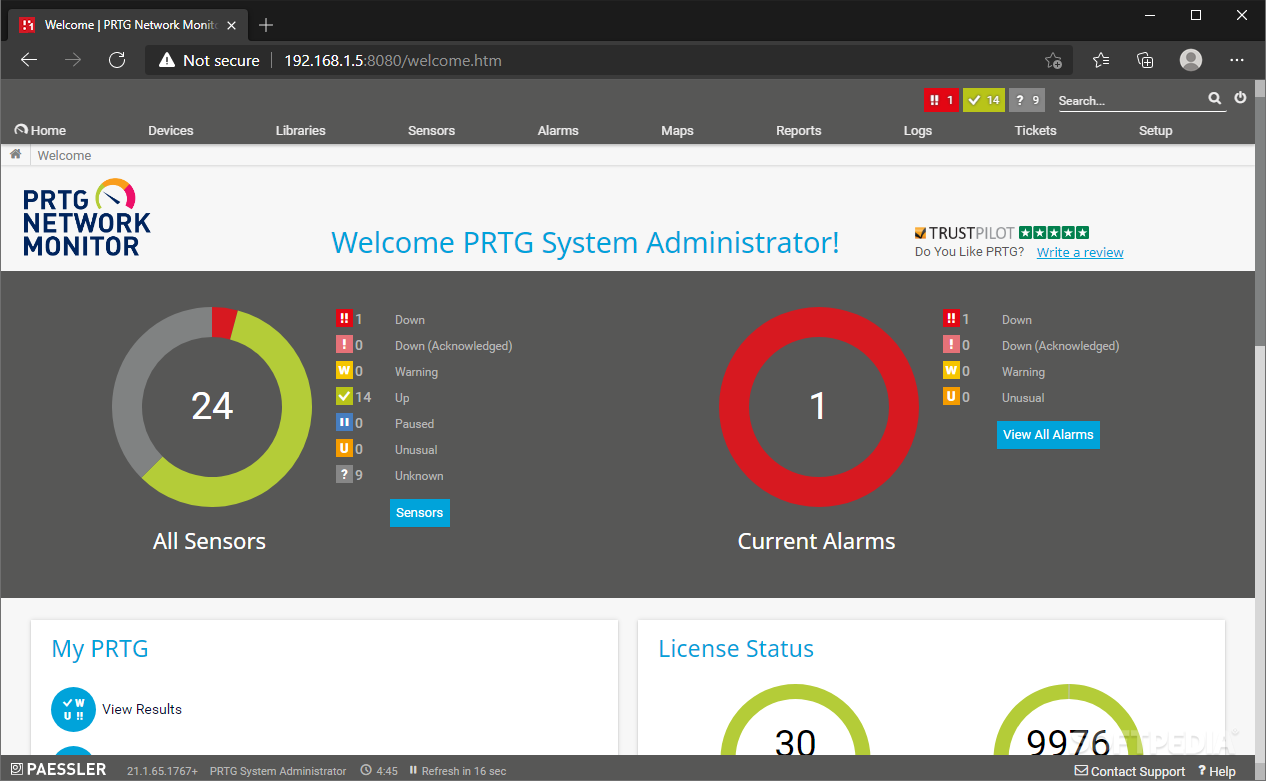
cat /proc/loadavg ).ĭefine which port this sensor will use for the SSH connection. This is the time in seconds the sensor waits for the shell to return a response after it has sent its specific command (e.g. You should keep this value as low as possible.ĭefine a timeout for the shell response.

This is the the time the sensor waits to establish a connection to the host. Note: If not set explicitly in a sensor's settings, it will connect to the IP Address or DNS Name defined in the settings of the parent device the sensor is created on.ĭefine a timeout for the connection. On the sensor's details page, click on the Settings tab to change settings. You can change all settings in the sensor's Settings tab later. Therefore, you will not see all setting fields in this dialog. It only shows the setting fields that are imperative for creating the sensor. The Add Sensor dialog appears when adding a new sensor on a device manually. Note: Not all Linux/Unix and Mac OS distributions can be supported by this sensor type.įor a general introduction to SSH monitoring, please see Monitoring via SSH section.
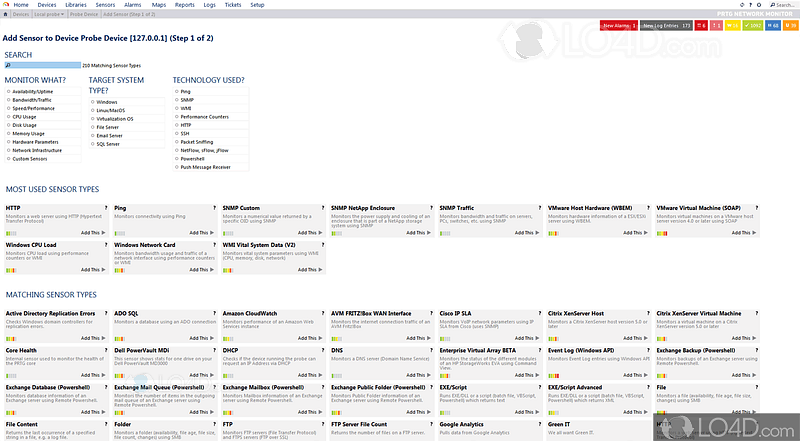
It can show packet loss, as well as minimum, maximum, and average response times all measured from the remote device you connect to.įor this sensor type credentials for Linux (SSH/WBEM) systems must be defined for the device you want to use the sensor on. The SSH Remote Ping sensor remotely monitors the connectivity between a system running Linux/OS X and an other device, using Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo requests ("Ping") and Secure Shell (SSH).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
